Differenze Tra Present Simple E Present Continuous

Capita a tutti di trovarsi di fronte a due opzioni apparentemente simili ma con sfumature che cambiano completamente il significato. Nello studio dell'inglese, uno di questi casi è rappresentato dal Present Simple e dal Present Continuous. Entrambi si riferiscono al presente, ma il loro uso corretto è fondamentale per esprimersi in modo chiaro e preciso. Cerchiamo di districarci insieme tra queste due forme verbali!
Che cos'è il Present Simple?
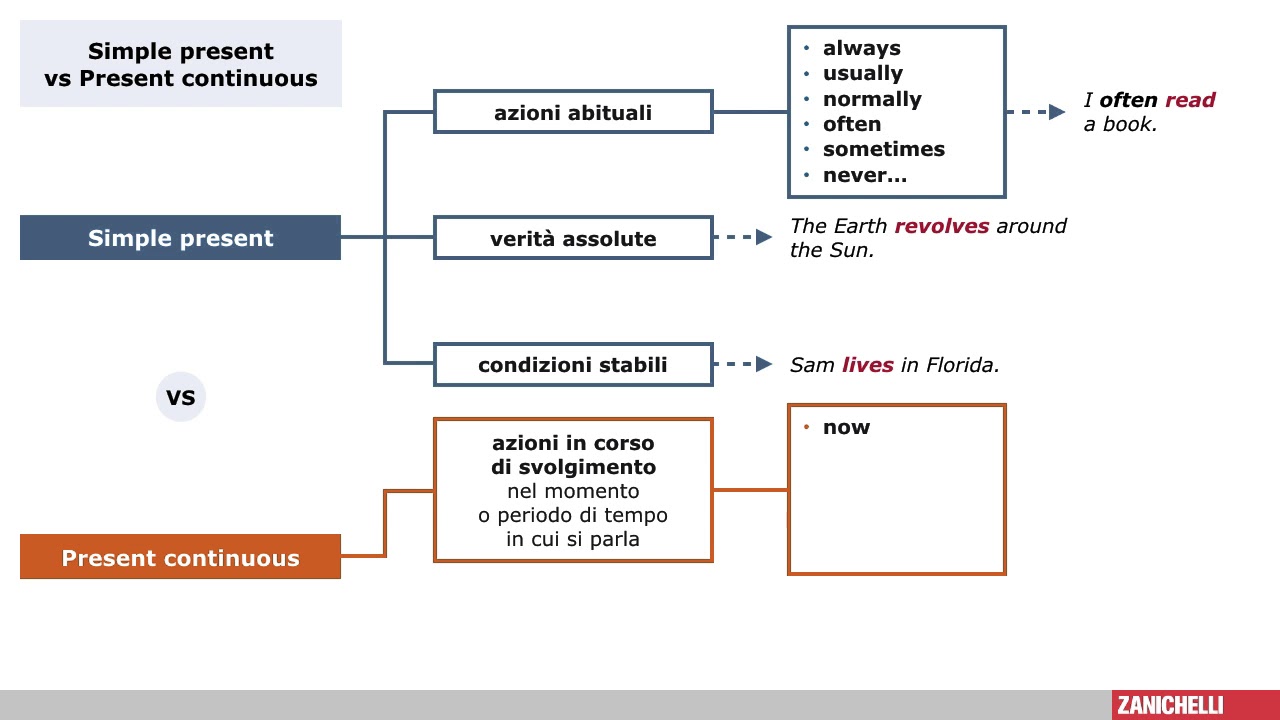
Il Present Simple è il tempo verbale più basico per esprimere azioni abituali, fatti generali e verità universali. Pensateci come alla colonna portante delle vostre conversazioni quotidiane, quella che descrive la routine, i gusti e le affermazioni che valgono sempre.
Quando Usare il Present Simple:
- Abitudini e routine: I wake up at 7 am every day. (Mi sveglio alle 7 ogni giorno.)
- Fatti generali e verità universali: The sun rises in the east. (Il sole sorge a est.)
- Orari e programmi fissi: The train leaves at 10:00 am. (Il treno parte alle 10:00.)
- Stati permanenti: I live in Rome. (Vivo a Roma.)
Notate come queste azioni o stati sono tipicamente ripetuti o costanti nel tempo. Non sono necessariamente in corso nel momento in cui si parla.
Come si forma il Present Simple:
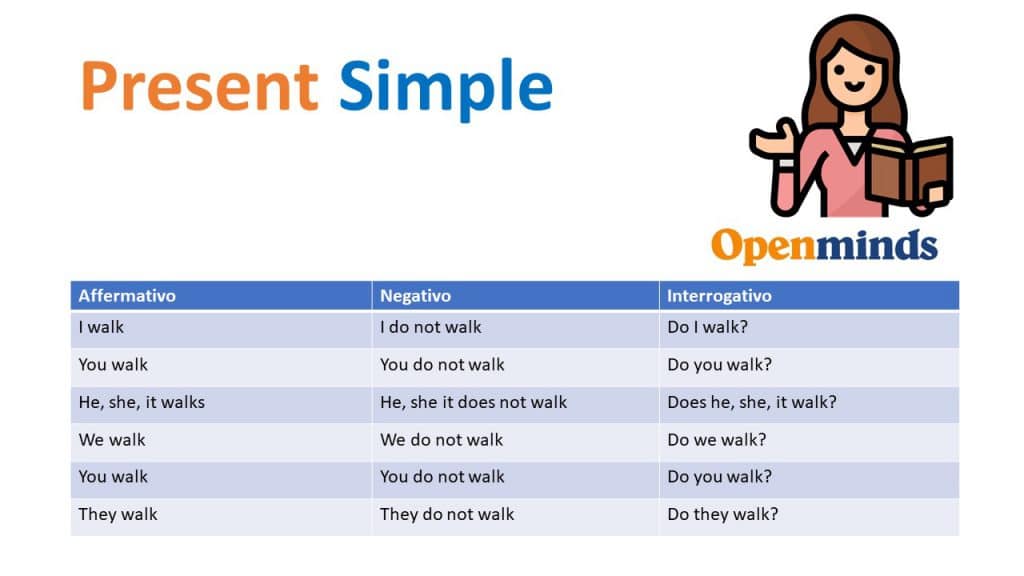
La formazione è piuttosto semplice. Generalmente, si usa la forma base del verbo. L'unica eccezione è la terza persona singolare (he, she, it), dove si aggiunge una "-s" o "-es" alla fine del verbo.
- I work
- You work
- He/She/It works
- We work
- They work
Per le forme negative e interrogative, si usano gli ausiliari "do" e "does" (per la terza persona singolare).
- I do not work (I don't work)
- Do you work?
- He/She/It does not work (He/She/It doesn't work)
- Does he/she/it work?
Che cos'è il Present Continuous?
Il Present Continuous, a volte chiamato anche Present Progressive, si concentra su azioni che stanno accadendo esattamente ora, nel momento in cui si parla, o su azioni che sono in corso di svolgimento in un periodo di tempo limitato e vicino al presente. Immaginatelo come una fotografia di un'azione in divenire.
Quando Usare il Present Continuous:
- Azioni in corso nel momento in cui si parla: I am writing this article right now. (Sto scrivendo questo articolo proprio ora.)
- Azioni temporanee: I am studying Italian this semester. (Sto studiando italiano questo semestre.)
- Piani futuri ben definiti: We are going to the cinema tonight. (Andiamo al cinema stasera.)
- Azioni che irritano (spesso con "always" o "constantly"): He is always complaining! (Si lamenta sempre!)
Queste azioni non sono abitudini fisse, ma eventi limitati nel tempo o piani specifici.
Come si forma il Present Continuous:
La sua formazione prevede l'uso del verbo "to be" (am, is, are) seguito dal verbo principale nella forma "-ing" (participio presente).
- I am working
- You are working
- He/She/It is working
- We are working
- They are working
La forma negativa si ottiene aggiungendo "not" dopo il verbo "to be", e per le domande si inverte l'ordine tra il soggetto e il verbo "to be".
- I am not working (I'm not working)
- Are you working?
- He/She/It is not working (He/She/It isn't working)
- Is he/she/it working?
Differenze Chiave e Consigli Pratici
La principale differenza tra i due tempi verbali risiede nella durata e nella ripetizione. Il Present Simple descrive azioni abituali e permanenti, mentre il Present Continuous si concentra su azioni temporanee e in corso.
Ecco alcuni punti cruciali da tenere a mente:
- Tempo: Present Simple per azioni ripetute e stati permanenti; Present Continuous per azioni in corso o temporanee.
- Abitudine vs. Azione: "I eat breakfast every morning" (Present Simple, abitudine) vs. "I am eating breakfast now" (Present Continuous, azione in corso).
- Piani Futuri: il Present Continuous può essere usato per piani futuri ben definiti, mentre il Present Simple per orari e programmi fissi.
Esempi Confrontati:
Consideriamo questi esempi per chiarire ulteriormente le differenze:
- Present Simple: She plays the piano. (Lei suona il piano – abilità generale.)
- Present Continuous: She is playing the piano right now. (Lei sta suonando il piano proprio ora – azione in corso.)
- Present Simple: They live in London. (Vivono a Londra – stato permanente.)
- Present Continuous: They are living in London for a few months. (Vivono a Londra per alcuni mesi – situazione temporanea.)
Verbi di Stato vs. Verbi di Azione
Un aspetto importante da considerare è la distinzione tra verbi di stato e verbi di azione. I verbi di stato descrivono sentimenti, opinioni, sensi e stati mentali (es. know, believe, love, hate, see, hear, smell, taste). Generalmente, questi verbi non vengono usati al Present Continuous, a meno che non cambino significato.
Ad esempio:
- Corretto: I know the answer. (So la risposta.)
- Incorretto (nella maggior parte dei casi): I am knowing the answer.
Tuttavia, alcuni verbi di stato possono essere usati al Present Continuous se descrivono un'azione, piuttosto che uno stato.
Ad esempio:
- Stato: I see what you mean. (Capisco cosa intendi.)
- Azione: I am seeing my doctor tomorrow. (Vado dal mio medico domani – appuntamento.)
Parole Chiave
Alcune parole chiave possono aiutarvi a identificare quale tempo verbale usare:
- Present Simple: always, usually, often, sometimes, rarely, never, every day/week/month/year.
- Present Continuous: now, at the moment, right now, today, this week/month/year.
Esercizi Pratici
Per consolidare la vostra comprensione, provate a completare questi esercizi:
- She _______ (work) in a bank.
- They _______ (watch) TV at the moment.
- He _______ (not/like) coffee.
- We _______ (go) to Italy next summer.
- _______ you _______ (study) English?
Risposte: 1. works, 2. are watching, 3. doesn't like, 4. are going, 5. Are, studying
Conclusione
Padroneggiare il Present Simple e il Present Continuous è fondamentale per comunicare in inglese in modo efficace. Ricordatevi di considerare il contesto, la durata dell'azione e la natura dei verbi (stato vs. azione). Con un po' di pratica, sarete in grado di usare questi due tempi verbali con sicurezza e naturalezza! Non abbiate paura di sperimentare e di fare errori. L'apprendimento di una lingua è un viaggio, non una destinazione.